Quit-Smoking Tips
Which Twin Is the Smoker?
Maybe there is no fountain of youth, but there is a surefire way to make yourself look older. Smoking changes the skin, teeth, and hair in ways that can add years to your looks. It also affects everything from your fertility to the strength of your heart, lungs, and bones. Take a look at these side-by-side photos. Can you pick out the smoker? Check your pick and get a closer look on the next slide.Tobacco's Tell-Tale Signs
Twin B smoked half a pack a day for 14 years, while her sister never smoked. The loose skin under her eyes is typical for smokers, according to Bahman Guyuron, MD, of Case Western Reserve University. It's one of several visible signs -- shown on the following slides -- that tobacco byproducts inside your body are harming your appearance. Twin B also got more sun, damaging her skin from the outside, too.Poor Skin Tone
Smoking chronically deprives the skin of oxygen and nutrients. So some smokers appear pale, while others develop uneven coloring. These changes can begin at a young age, according to dermatologist Jonette Keri, MD, of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. "In young nonsmokers, we don't usually see a lot of uneven skin tone," Keri says. "But this develops more quickly in people who smoke."Sagging Skin
There are more than 4,000 chemicals in tobacco smoke, and many of them trigger the destruction of collagen and elastin. These are the fibers that give your skin its strength and elasticity. Smoking or even being around secondhand smoke "degrades the building blocks of the skin," Keri says. The consequences include sagging skin and deeper wrinkles.Sagging Arms and Breasts
Smoking doesn't only damage the appearance of your face, it can also take a toll on your figure. As skin loses its elasticity, parts that were once firm may begin to droop. This includes the inner arms and breasts. Researchers have identified smoking as a top cause of sagging breasts.Lines Around the Lips
Smoking delivers a one-two punch to the area around your mouth. First, you have the smoker's pucker. "Smokers use certain muscles around their lips that cause them to have dynamic wrinkles that nonsmokers do not," Keri says. Second, you have the loss of elasticity. Together, these factors can lead to deep lines around the lips.Age Spots
Age spots are blotches of darker skin color that are common on the face and hands. While anyone can develop these spots from spending too much time in the sun, research suggests smokers are more susceptible.
In this image, the twin on the right spent decades smoking and sunbathing, while her sister did not. Damaged Teeth and Gums
Yellow teeth are one of the most notorious effects of long-term smoking, but the dental damage doesn't stop there. People who smoke tend to develop gum disease, persistent bad breath, and other oral hygiene problems. Smokers are twice as likely to lose teeth as nonsmokers.Stained Fingers
Think your hand looks sexy with a cigarette perched between your fingers? If you've been smoking for awhile, take a good look at your fingernails and the skin of your hands. Tobacco can actually stain the skin and nails, as well as the teeth. The good news is these stains tend to fade when you quit smoking.Hair Loss
Both men and women tend to develop thinner hair as they age, and smoking can accelerate this process. Some studies even suggest people who smoke are more likely to go bald. Researchers in Taiwan have identified smoking as a clear risk factor for male-pattern baldness in Asian men.Cataracts
Even the eyes are vulnerable to tobacco's reach. Smoking makes you more likely to develop cataracts as you age. These are cloudy areas on the lens of the eye that keep light from reaching the retina. If they cause serious vision problems, they are treated with surgery.Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that most often causes thick, scaly patches on the skin -- usually on the knees, elbows, scalp, hands, feet, or back. The patches may be white, red, or silver. Recent studies suggest smokers have a greater risk of developing psoriasis.Crow's Feet Eye Wrinkles
Everyone gets wrinkles on the outside of the eyes eventually, but these wrinkles develop earlier and go deeper among smokers. Heat from burning cigarettes and squinting to keep smoke out of your eyes contribute to visible crow's feet. Meanwhile, chemicals from inhaled tobacco cause internal damage to the skin structures and blood vessels around your eyes.How Quitting Improves Your Looks
Quitting smoking can improve your appearance. As blood flow gets better, your skin receives more oxygen and nutrients. This can help you develop a healthier complexion. If you stay tobacco-free, the stains on your fingers and nails will disappear. You may even notice your teeth getting whiter.Combating Skin Damage: Creams
When you quit smoking, you make your skin more resistant to premature aging. As for the wrinkles and age spots you already have, all is not lost. Keri, the University of Miami dermatologist, says there are products former smokers can use to make their skin look better. These include topical retinoids and antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E. She also recommends wearing sunscreen every day.Combating Skin Damage: Procedures
For more dramatic results, some former smokers choose to have cosmetic procedures. Laser skin resurfacing and chemical peels remove outer layers of skin, where the damage is most visible. "Reward yourself with a couple of skin treatments," Keri suggests. "When you see the benefits of better-looking skin, you may be motivated to stay nicotine-free."Brittle Bones
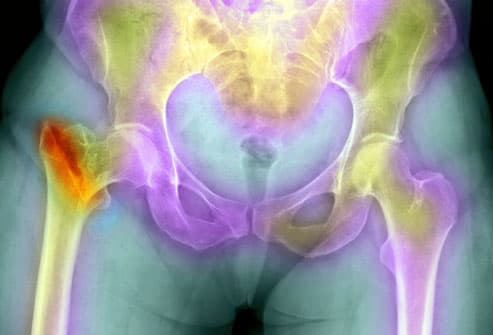
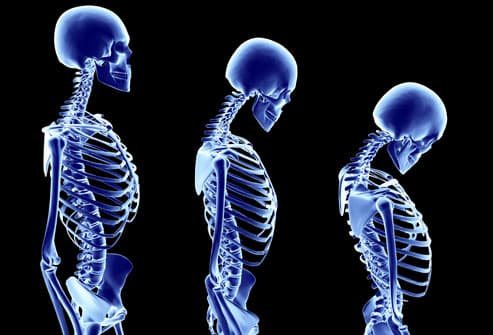
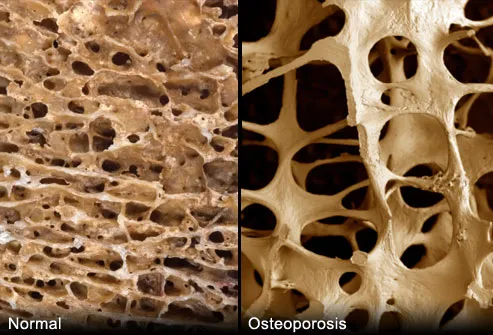
Everyone knows the lungs take a beating from smoking, but research has pinpointed additional, surprising ways that tobacco affects the body, starting with your bones. Smoking raises your risk of developing weakened bones, or osteoporosis. This condition increases your risk for bone fractures including those of the spine, causing it to curve and leaving you hunched over.Heart Disease and ED
Smoking affects nearly every organ in the body, including the heart. In people who smoke, the arteries that carry blood to the heart become narrowed over time. Smoking also increases blood pressure and makes it easier for blood to clot. These factors raise the odds of having a heart attack. In men who smoke, reduced blood flow can lead to erectile dysfunction.Reduced Athletic Ability
Smoking's impact on the heart and lungs can add up to a significant disadvantage on the track or field. Smokers tend to have a more rapid heart rate, poorer circulation, and more shortness of breath -- not helpful qualities in an athlete. Whatever your favorite sport, one way to enhance your performance is to quit smoking.Reproductive Problems
Women who smoke have a tougher time getting pregnant and giving birth to a healthy baby. Cigarettes have been linked to fertility problems. And smoking during pregnancy raises the odds of having a miscarriage, premature birth, or delivering a low-birth-weight infant.Early Menopause
It's something all women have in common: menopause, the phase when female hormones decline and the menstrual cycle stops for good. Most women experience this change around age 50. But smokers reach menopause an average of 1 1/2 years earlier than women who don't smoke. The effect is strongest in women who have smoked heavily for many years.Oral Cancer
Compared to nonsmokers, people who smoke or use smokeless tobacco products are more likely to develop oral cancer. Smokers who are also heavy drinkers are 15 times more likely to develop this form of cancer. The most common symptoms include a sore patch on the tongue, lips, gums, or other area inside the mouth that doesn't go away and may be painful. Quitting smoking lowers the risk for oral cancer substantially within a few years.Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the top cancer killer of men and women in the U.S. Of those who die from the disease, 9 out of 10 deaths are due to smoking. Cigarettes can also damage the lungs in other ways, making people more vulnerable to breathing problems and dangerous infections like pneumonia.How Quitting Improves Your Health
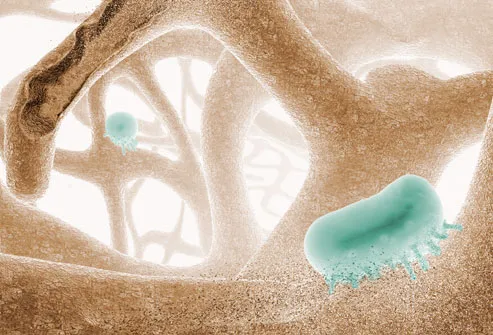
In just 20 minutes, blood pressure and heart rate return to normal. Within 24 hours, your heart attack risk begins falling. In the first weeks after quitting, tiny cilia (seen here) start back to work sweeping irritants out of the lungs. Within a year, your risk of developing heart disease drops to half that of people who still smoke. And after 10 smoke-free years, you're no more likely to die of lung cancer than someone who never smoked.Cigarette Stench
Quitting eliminates the pervasive smell of cigarettes on your breath and in your hair and clothes. This is unattractive to nonsmokers and carries health hazards, too. The odor means that the people around you are exposed to tobacco toxins, sometimes called "third-hand smoke." These toxins can be especially harmful to small children.Can You Quit?
Experts agree that giving up cigarettes is very difficult. But if you're telling yourself it's impossible, think again. While there are 45 million smokers in the U.S., there are at least 48 million
former smokers. If 48 million people could quit, it is doable. Just keep in mind that most people have to try more than once, and only 4%-7% succeed without help. Ask your doctor which smoking-cessation strategies might be right for you.
THE SMOKING HABIT MAY BE MANAGED BY USING HOMEO MEDICINES AS GIVEN BELOW;
1-TABACUM 200 DAILY DOSE OR
2-CALADIUM 200 DAILY DOSE OR
ALL THESE HOMEO MEDICINES ARE USED ACCORDING TO THE INDIVIDUAL SYMPTIOMS SO IT IS ADVISED TO CONSULT YOUR NESREST HOME DOCTOR OR WRITE US ;
HDAA09@YAHOO.COM.